Multi-Agent AI Platforms: The Collaborative Future of Enterprise Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence has progressed remarkably from narrow, rule-based systems to advanced, autonomous models capable of human-like reasoning. However, as businesses and digital ecosystems become increasingly complex, the need has emerged for AI systems that not only solve problems independently but also collaborate, negotiate, and reason collectively. This marks the rise of multi-agent AI platforms—a transformative step forward in artificial intelligence architecture. At their core, these systems are composed of multiple autonomous or semi-autonomous agents working in concert to achieve a broader set of objectives than any single model could achieve alone. When implemented within enterprise environments—like in the case of the Purple Fabric platform—multi-agent AI becomes a powerful engine for delivering secure, decision-grade intelligence at scale.
The Concept of Multi-Agent AI: Beyond Individual Intelligence
Traditional AI systems often function as isolated models, designed to perform specific tasks within predefined boundaries. While effective in narrow applications, these standalone models struggle to adapt to complex, dynamic environments where decisions require contextual awareness, collaboration, and continuous learning. This is where multi-agent AI redefines the paradigm.
A multi-agent AI system comprises multiple autonomous or semi-autonomous agents—each with its own intelligence, role, and goal—working together within a shared environment. These agents can communicate, collaborate, and even negotiate with one another to solve problems that are too large or too complex for a single system to handle alone. Unlike monolithic AI, the intelligence in a multi-agent system is distributed. Insights emerge not from one central brain, but from the interplay and coordination among agents.
This agent-based approach mirrors real-world ecosystems, where diverse actors interact and adapt in real time. In enterprise scenarios, such as underwriting, supply chain management, or fraud detection, multiple AI agents can handle different stages of a workflow—extracting data, analyzing context, generating decisions, and validating outputs. The result is a scalable, flexible, and collaborative AI architecture that goes far beyond the limitations of single-model intelligence, paving the way for more responsive, human-aligned AI systems.
The Architecture of a Multi-Agent AI System
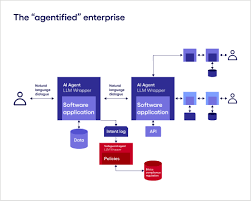
The architecture of a multi-agent AI system is designed to enable autonomous agents to function collaboratively within a shared environment while maintaining the flexibility to act independently. At its core, this architecture is distributed and modular, allowing each agent to operate with localized intelligence while contributing to a larger, coordinated objective.
A typical system includes several key layers. First is the environment or knowledge base, a central repository where agents access data, context, and historical interactions. Agents interact with this shared environment to perceive situations, retrieve information, or update knowledge in real time. Each agent is equipped with capabilities such as sensing, reasoning, learning, and acting, often powered by task-specific models or large language models (LLMs).
Communication is facilitated through a messaging or orchestration layer, which manages agent interactions, synchronizes workflows, and resolves conflicts. This layer ensures agents can collaborate, escalate tasks, or negotiate decisions effectively.
Additionally, an orchestration engine governs how agents are deployed, sequenced, and scaled across workflows. Platforms like Purple Fabric enhance this architecture by integrating governance, security, and explainability, ensuring every agent action is traceable and compliant.
This architecture enables organizations to build resilient, intelligent systems that are adaptable, scalable, and aligned with evolving business goals.
Why Multi-Agent AI Matters for Enterprises
As enterprises grapple with growing data complexity, fragmented workflows, and the need for rapid decision-making, traditional AI systems often fall short. They are typically designed as monolithic models optimized for isolated tasks, offering limited flexibility and scalability. In contrast, multi-agent AI introduces a new operational paradigm—one that aligns far more effectively with the dynamic needs of modern businesses.
Multi-agent AI systems consist of autonomous, intelligent agents that specialize in specific functions yet work together as part of a broader, orchestrated intelligence framework. This collaborative model offers significant advantages for enterprises. It enables parallel processing of tasks, adaptability to changing inputs, and continuous learning from interactions across systems and agents.
For example, in complex domains like insurance, banking, or logistics, different agents can handle data extraction, policy checks, compliance validation, and customer interaction—all within a single automated flow. This leads to faster decision cycles, reduced operational costs, and greater accuracy. Moreover, the modular nature of agent-based systems means businesses can scale specific functions without overhauling the entire platform.
Platforms like Purple Fabric demonstrate how multi-agent AI can turn fragmented business operations into integrated, intelligent ecosystems. By empowering domain experts to create, configure, and monitor AI agents, enterprises gain a resilient, agile, and explainable AI infrastructure that delivers measurable business impact—securely and at scale.
From AI Models to AI Agents: A Paradigm Shift
The evolution from traditional AI models to intelligent agents marks a significant paradigm shift in how organizations build and deploy artificial intelligence. AI models, such as classifiers or predictive algorithms, are typically static and task-specific. They require precise inputs, deliver narrow outputs, and operate in isolation. While powerful, these models lack the flexibility, context-awareness, and interactivity needed for complex enterprise environments.
AI agents, on the other hand, represent a new breed of intelligent systems. They are goal-driven, autonomous, and capable of reasoning, learning, and acting within dynamic environments. Unlike static models, agents can interact with other agents, access enterprise knowledge, adapt to new data, and even delegate or escalate tasks based on outcomes. They operate more like digital employees than mere algorithms.
This shift is particularly transformative in enterprise settings. Platforms like Purple Fabric empower subject-matter experts to build, orchestrate, and deploy AI agents using low-code tools. These agents are not just model wrappers—they are intelligent entities capable of navigating workflows, making decisions, and evolving over time.
By moving from models to agents, organizations unlock greater flexibility, scalability, and business alignment. This agent-based approach allows enterprises to create intelligent, collaborative systems that mirror human processes—enhancing efficiency while maintaining transparency and control.
Governance and Trust in Multi-Agent AI Systems
As AI systems become more autonomous, governance becomes indispensable. Multi-agent AI platforms introduce added complexity since multiple agents interact, share data, and influence outcomes. Without robust oversight, these interactions could lead to unforeseen consequences, bias propagation, or security vulnerabilities.
Enterprise-grade platforms must therefore embed governance frameworks that ensure every agent’s action is auditable, explainable, and aligned with organizational values and regulations. In Purple Fabric, for example, every decision made by an agent is traceable through logs, dashboards, and audit trails. The platform incorporates guardrails such as data masking, policy enforcement, and model-level explainability—ensuring not only functional performance but also compliance and trustworthiness.
Governance also supports model risk management. Since Purple Fabric is LLM-agnostic, organizations can benchmark different models within agents, monitor their outputs, and switch models as needed—balancing performance with cost, latency, and safety.
The Road Ahead: Toward Autonomic Enterprises
Looking forward, the evolution of multi-agent AI platforms will drive enterprises toward autonomic systems—AI-enabled organizations that are self-configuring, self-optimizing, and self-healing. In such environments, agents won’t just follow static instructions; they’ll learn from operational data, propose process improvements, and dynamically optimize workflows in real time.
We are also seeing the rise of human-agent teams, where employees and AI agents collaborate seamlessly. In this setup, the AI handles repetitive or data-intensive tasks, freeing humans to focus on strategy, creativity, and interpersonal dynamics. Multi-agent systems become the connective tissue, ensuring information flows and decisions are synchronized across people and machines.
As technologies like edge computing, federated learning, and digital twins mature, agents will increasingly be deployed not only in cloud-based systems but also at the edge—on devices, vehicles, and machinery—allowing for local, context-sensitive decision-making.
Conclusion: A Future Built on Collaboration
The future of AI lies not in isolated supermodels, but in collaborative, explainable, and goal-driven agent ecosystems. Multi-agent AI platforms offer a scalable, modular, and intelligent approach to enterprise automation and augmentation. They go beyond mere efficiency to enable strategic transformation—turning businesses into intelligent organisms capable of learning, adapting, and thriving in dynamic markets.
Platforms like Purple Fabric exemplify this shift. They bring together data, intelligence, governance, and human expertise in a unified fabric—where agents can be created, deployed, and managed with business objectives at the core. Whether it’s underwriting, customer service, fraud detection, or operational optimization, these platforms prove that agentic intelligence isn’t just the next step in AI—it’s the foundation of the intelligent enterprise.
In embracing multi-agent AI, organizations are not merely adopting a new technology—they are stepping into a new era of collaborative, measurable, and sustainable intelligence. And in this era, every interaction, every workflow, and every decision becomes an opportunity to create impact—securely, transparently, and at scale.

Source: Multi-Agent AI Platforms: The Collaborative Future of Enterprise Intelligence




